By Ted Rosen, MD, FAAD, Editor-in-Chief
Research updates in pediatric dermatology, infectious diseases, rheumatologic diseases, hidradenitis suppurativa, cutaneous oncology, and more
Several reports have described a transverse red-violet nail band located just above the normal lunula as a sign of COVID-19 infection. To read more: Mendez-Flores S, et al. COVID-19 and nail manifestations: be on the lookout for the red half-moon nail sign. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1414.
Disproportionate to population percentage, in many states, black individuals have higher prevalence of COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and death. To read more: Kullar R, et al. Racial disparity of coronavirus disease 2019 in African American communities. J Infect Dis. 2020;222:890-93.
A Spanish observational study of more than 11,000 COVID-19-positive individuals who required hospitalization disclosed that hyperglycemia at the time of admission was a strong predictor of poor outcome. Patients with admission hyperglycemia were more likely to progress from noncritical to critical condition and death, regardless of prior diabetes history. To read more: Carrasco-Sanchez FJ, et al. Admission hyperglycemia as a predictor of mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 regardless of diabetes status: data from the Spanish SEMI-COVID-19 Registry. Annal Med. Nov 2020. DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1836566
COVID-19 has become the leading overall cause of death in the US. Heart disease and cancer lead to about 1700 and 1600 deaths daily, respectively. However, COVID-19 deaths have now surpassed both these numbers, with more than 3000 daily deaths. To read more: Woolf SH, et al. COVID-19 as the leading cause of death in the United States. JAMA. 2020 Dec 17. DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.24865
CDC analytical modeling discloses that 59% of all COVID-19 transmission comes from individuals who are asymptomatic. The importance of this finding is that identification and rapid isolation of individuals displaying symptoms of COVID-19 will not stop the persistence of this pandemic. To read more: Johansson MA, et al. SARS-CoV-2 transmission from people without COVID-19 symptoms. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2035057. DOI:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057

Even extensive bedbug bites can be successfully managed by administration of ultrapotent topical steroids and oral non-sedating antihistamines (to tolerance). Eradication of an infestation requires both insecticide and physical modalities. To read more: Delaunay P, et al. Bed bug bites. Dermatol Ther. 2020 Sep 25. DOI: 10.1111/dth.14341
Evidence for the utility of popular oral hair growth supplements is weak, at best. A recent comprehensive summary summarized: No clinical evidence supports the use of vitamins A, C, and D, biotin, niacin, selenium, ashwagandha, curcumin, and capsaicin; iron supplements should be given when known iron deficiency exists; conflicting data exists for use of zinc in hair loss; weak evidence exists for the use of vitamin E in multiple hair loss conditions; weak evidence exists for pumpkin seed oil and saw palmetto in androgenetic alopecia; horsetail and methylsulfonylmethane supplementation may improve hair health; and marine complexes have exhibited positive effects on hair health. To read more: Adelman MJ, et al. Clinical efficacy of popular oral hair growth supplement ingredients. Int J Dermatol. 2020 Dec 9. DOI: 10.1111/ijd.15344
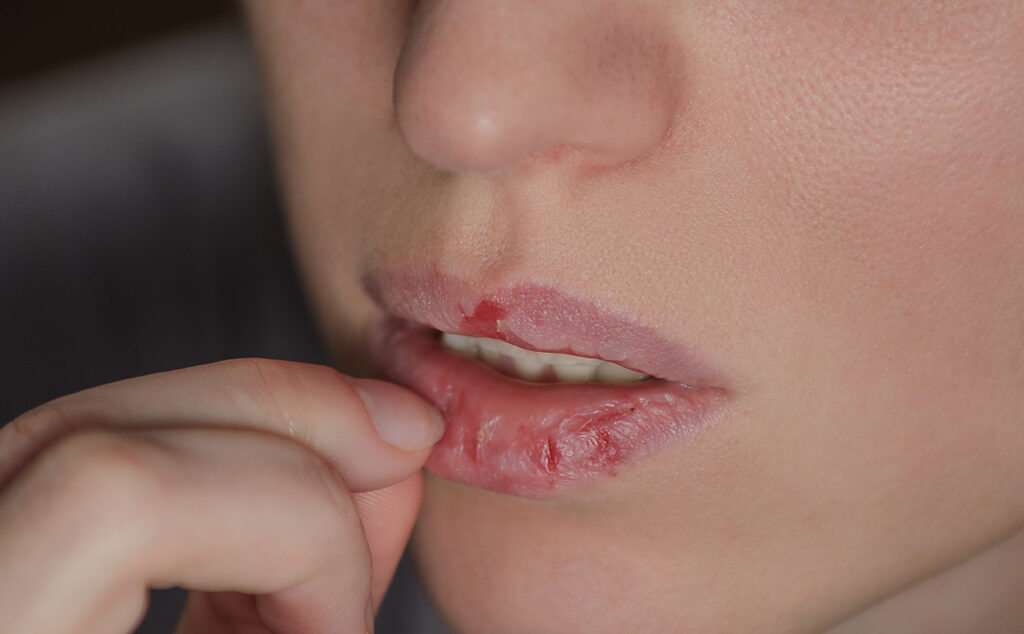
Chronic lip-licking can lead to irritant contact dermatitis, secondary infections, and various forms of cheilitis. The most important suggested preventative maneuver is daily application of a bland lip balm that has minimal amounts of dyes, fragrances, and flavorants, but is rich in ceramides, shea butter, petrolatum, or dimethicone. Cognitive behavioral therapy may also help break the habit of chronic picking at dry lips. To read more: Fonseca A, et al. Art of prevention: practical interventions in lip-licking dermatitis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6(5):377-80.
A meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled and 13 prospective observational studies, including 2445 patients, indicated that acne patients have lower serum zinc levels than age-matched controls. Oral zinc therapy appears to be beneficial in this analysis of English-language literature. Optimal formulation, dose, and duration of therapy have yet to be determined definitively. To read more: Yee BE, et al. Serum zinc levels and efficacy of zinc treatment in acne vulgaris: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Dermatol Ther. 2020 Aug 29;e14252. DOI: 10.1111/dth.14252
A small, double blind, placebo-controlled Thai study suggests that twice daily application of ketoconazole cream 2% may benefit mild adult female acne. Ketoconazole is anti-fungal, but also inherently anti-inflammatory and antiandrogenic; it can also inhibit Cutibacterium acnes lipase activity. To read more: Chottawornsak N, et al. Topical 2% ketoconazole cream monotherapy significantly improves adult female acne: a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Dermatol. 2019;46(12):1184-1189.
Concurrent daily application of oxymetazoline hydrochloride 1% cream may enhance the benefit of a wide range of light and laser treatments when utilized for management of persistent facial erythema associated with rosacea. To read more: Tanghetti EA, et al. Oxymetazoline and energy‐based therapy in patients with rosacea: evaluation of the safety and tolerability in an open‐label, interventional study. Lasers Surg Med. 2020 May 6. DOI: 10.1002/lsm.23253
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s Disease patients have a 3-fold greater risk of developing rosacea compared to age/sex matched individuals who do not have inflammatory bowel disease. To read more: Daou H, et al. Rosacea and the microbiome: a systematic review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Nov 10. DOI: 10.1007/s13555-020-00460-1

