BRAF mutations in skin cancers may help repair cardiac muscle after a heart attack, according to a study in Science Advances.
BRAF is a part of the MAPK signaling pathway that can promote cell division, In a new study, researchers show that introducing this mutation to rat heart tissue grown in a laboratory can induce growth.
“Mature heart muscle cells do not typically divide, so we thought we’d need an especially strong genetic mutation to convince them to multiply,” explains Nenad Bursac, professor of biomedical engineering at Duke University in Durham, NC, in a news release. “MAPK is a well understood pathway that, when mutated, can be pretty aggressive at inducing proliferation in cancers, which is why we chose to look into it.”
For the study, Bursac and PhD student Nicholas Strash studied neonatal rat heart cells grown within a 3D hydrogel environment. Developed by the laboratory over more than a decade, the hydrogel environment provides the cues to grow and mature cells into adult-like heart muscle tissues, where cell division naturally stops.
Then, to try to get the muscle to divide and grow again, the researchers infected it with a virus loaded with a mutated BRAF gene. Following its normal behavior, the virus inserted the mutated gene into the cells, causing it to become a part of the cells’ DNA. The researchers then introduced a drug that caused the mutated BRAF genes to activate.
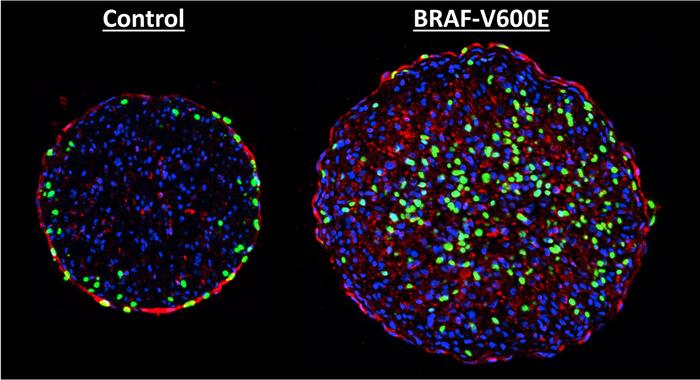
As with skin cancer, once activated, the mutant genes caused the heart muscle cells to enter DNA synthesis, but there were also drawbacks.
“Once the cells started entering into their multiplication phase, they also began disassembling the machinery that allows them to contract and pump blood when in the heart,” Strash says. “It caused the tissue as a whole to lose about 70% of its contractile strength, which is pretty dramatic. One reason for this is that almost all cells in the tissue got infected by the virus.”
There’s much to do before any potential use in human patients.
Due to the accompanying loss of strength, the dosage and duration of gene activation needs to be precisely controlled.
For starters, a different delivery system would have to be applied that can deliver the genes to the correct cells in a way that clinicians can fully control. Methods such as lipid nanoparticles and short-living viruses are two approaches currently being developed, but both still have a ways to go before they could be applied for heart regeneration in humans.
The other major hurdle is finding a way to jump start heart tissue regeneration without causing the tissue to lose strength. Based on the timing of cellular mechanisms, the researchers believe there may be a window in which the mutated gene activity could be stopped after the replication begins, but before the contractile machinery is affected in a large portion of the heart. Or there may be an opportunity to administer a second therapeutic that could prompt the cells to rebuild the dismantled pumping machinery after proliferation.
Moving forward, the researchers are planning to study how this approach works in the hearts of live animals and compare it to their lab-tested results. Working with live animals will also provide a better understanding of what other genes and processes are activated by the mutated BRAF gene, and whether proliferation could be independently activated without functional decline to efficiently promote healing.
“The heart essentially does not have primary cancers, and it’s almost unique that it doesn’t,” Bursac says. “Introducing this cancer mutation in the heart is obviously an engineered outcome that doesn’t happen naturally. Studying it in lab-grown tissues is a great step toward understanding what this entire signaling pathway does within the heart, which could have benefits beyond regenerative therapies.”
CAPTION: Two cross sections of engineered rat cardiac tissue showing the BRAF mutation at work. The BRAF-altered cell on the right has more newly synthesized DNA (green), showing the mutation is inducing cell division.