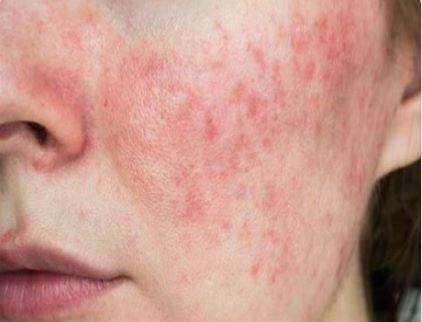
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Minocycline Hydrochloride Extended Release Capsules, 40 mg (Emrosi, Journey Medical Corporation), formerly referred to as DFD-29, for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of rosacea in adults.
Emrosi was developed in collaboration with Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd. Journey Medical is completing the manufacturing of Emrosi for the U.S. market and anticipates that initial supply will be available late in the first quarter or early in the second quarter of 2025.
“With approval from the FDA, Journey Medical is proud to deliver Emrosi, a unique treatment option for the millions of patients in the U.S. suffering from rosacea,” says Claude Maraoui, Co-Founder, President, and Chief Executive Officer of Journey Medical, in a news release. “Rosacea is a difficult to treat skin condition and based on the favorable results from our Phase 3 clinical trials, Emrosi has potential to become the best-in-class oral medication to treat the condition.”
The approval of Emrosi is supported by positive data from Journey Medical’s two Phase 3 clinical trials for the treatment of rosacea. The Phase 3 clinical trials met all co-primary and secondary endpoints, and subjects completed the 16-week treatment with no significant safety issues. Emrosi demonstrated statistically significant superiority over both the current standard-of-care treatment, Oracea 40 mg capsules (doxycycline, Galderma) and placebo for Investigator’s Global Assessment treatment success as well as the reduction in total inflammatory lesion count in both studies.