A Qin-Zhu-Liang-Xue (QZLX) decoction may help improve the symptoms of atopic dermatitis (AD), according to preclinical and clinical studies.
A Chinese herbal medicine, QZLX decoction is composed of 10 herbal and mineral medicines. The primary active ingredients, baicalin and glycyrrhizic acid, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Network pharmacology analysis identified the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) as a central target of QZLX.
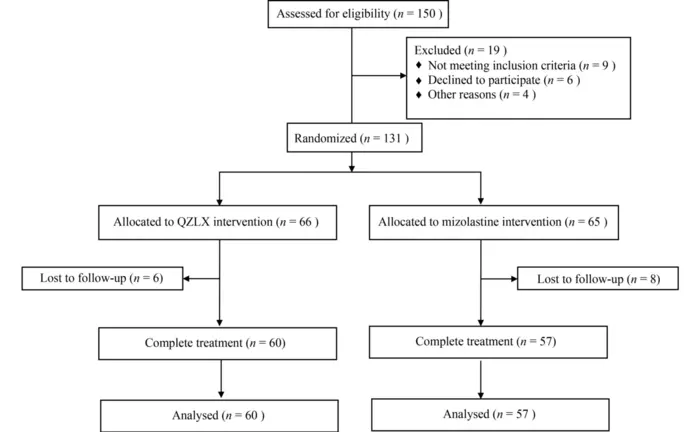
The study included a prospective, randomized trial with 131 patients, where the treatment group received QZLX decoction, and the control group received mizolastine. QZLX significantly improved AD symptoms, as indicated by reduced SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores, with no serious adverse effects.
Network pharmacology analysis revealed 361 overlapping genes between QZLX targets and AD-related genes, identifying core genes like NFKBIA and NR3C1. GRα, encoded by NR3C1, was validated as a key target, with QZLX treatment increasing its expression in patients’ serum.
Animal experiments using a DNFB-induced AD mouse model further confirmed QZLX’s efficacy. The decoction alleviated skin lesions, reduced scratching behavior, and improved pathological conditions. It also decreased inflammatory markers like IgE and cytokines, and increased Glucocorticoid receptor α (GRα) expression in skin lesions. These findings suggest QZLX mitigates AD by enhancing GRα expression and reducing inflammation.
The study is published in Frontiers of Medicine.
IMAGE CAPTION: Patient flow chart
IMAGE CREDIT: Keke Huang, Qingkai Liu, Ruoxi Zhang, Hua Nian, Ying Luo, Yue Luo, Xiaoya Fei, Le Kuai, Bin Li, Yimei Tan, Su Li, Xin Ma