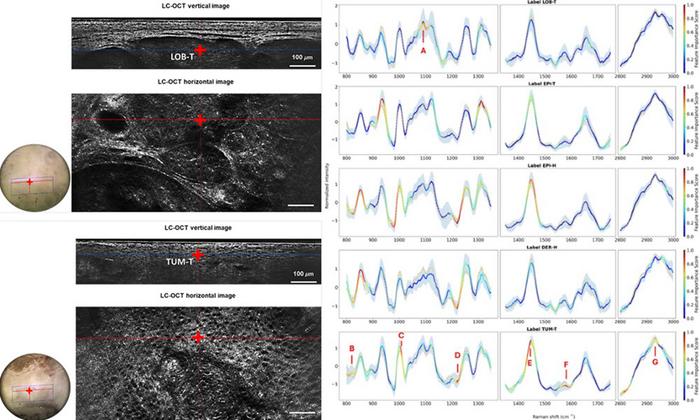
A compact, noninvasive imaging system combining line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT) and confocal Raman microspectroscopy may improve how doctors diagnose and classify skin cancer and monitor treatment responses.
LC-OCT captures high-resolution images of skin tissue at the cellular level, and confocal Raman microspectroscopy analyzes the chemical makeup of specific areas identified in those images. Together, these tools allow researchers to not only see the shape and structure of cancerous cells but also understand their molecular characteristics—without cutting into the skin.
The study is published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics.
The technology was developed by researchers at the Saint-Étienne University Hospital and Paris-Saclay University in collaboration with Damae Medical (France). The system has been tested in a clinical setting on more than 330 skin cancer samples, specifically nonmelanoma types like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The researchers used LC-OCT to locate suspicious structures and then applied Raman microspectroscopy to gather more than 1,300 chemical spectra from those areas. To interpret the data, they trained an artificial intelligence (AI) model to recognize patterns associated with cancerous tissues.
The AI model performed well, achieving a classification accuracy of 95% for basal cell carcinoma and 92% when both types of cancer were included. These results suggest the system can reliably distinguish cancerous structures based on their chemical signatures. Further analysis revealed distinct chemical differences between various cancer types, offering new insights into how these cancers develop and behave.
IMAGE CAPTION: Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT) captures high-resolution images of skin tissue at the cellular level, and then confocal Raman microspectroscopy analyzes the chemical makeup of specific areas identified in those images. Together, these tools enable insights into the shape and structure of cancerous cells.
IMAGE CREDIT: M. Ayadh et al., https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.30.7.076008