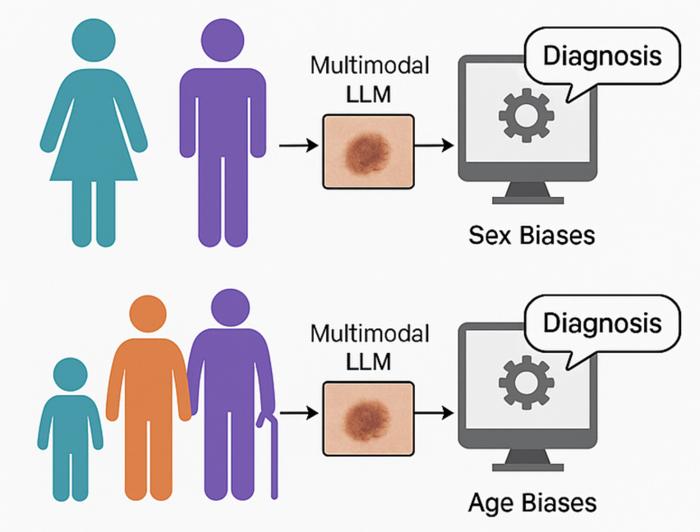
Large language models like ChatGPT-4 and LLaVA demonstrate potential in dermatology, but the utility of these models is limited by sex and age biases, according to research in Health Data Science.
What Did the Researchers Find?
Utilizing approximately 10,000 dermatoscopic images, the study focused on three common skin diseases: melanoma, melanocytic nevi, and benign keratosis-like lesions. ChatGPT-4 and LLaVA outperformed most traditional deep learning models overall, and ChatGPT-4 showed greater fairness across demographic groups, whereas LLaVA exhibited significant sex-related biases, the study found.
What’s the Next Step?
The team plans further research incorporating additional demographic variables like skin tone to comprehensively evaluate the fairness and reliability of AI models in clinical scenarios.
PHOTO CAPTION: Scientists from ShanghaiTech University compared the performance of large language models, like ChatGPT-4 and LLaVA, in diagnosing skin diseases among male and female patients across different age groups. The findings point to potential biases across age and sex groups that must be addressed before clinical deployment.
PHOTO CREDIT: Zhiyu Wan, Health Information Safety and Intelligence Research Lab, ShanghaiTech University (generated with the help of ChatGPT-4o).